Hixonparvo Models
Hixonparvo models are used to study parvovirus infections by simulating the conditions in which viruses infect host cells. These models allow for the observation of different stages of the viral replication cycle, including virus entry into cells, genome replication, and the assembly of viral particles. They are also used to analyze interactions between the virus and the host cell, focusing on viral attachment, entry mechanisms, and the impact of the virus on cellular functions, including immune responses. These models are valuable for testing the effectiveness of antiviral treatments by monitoring the impact of these treatments on viral replication and host response, as well as for vaccine development by evaluating how vaccines stimulate the immune system to fight the infection.
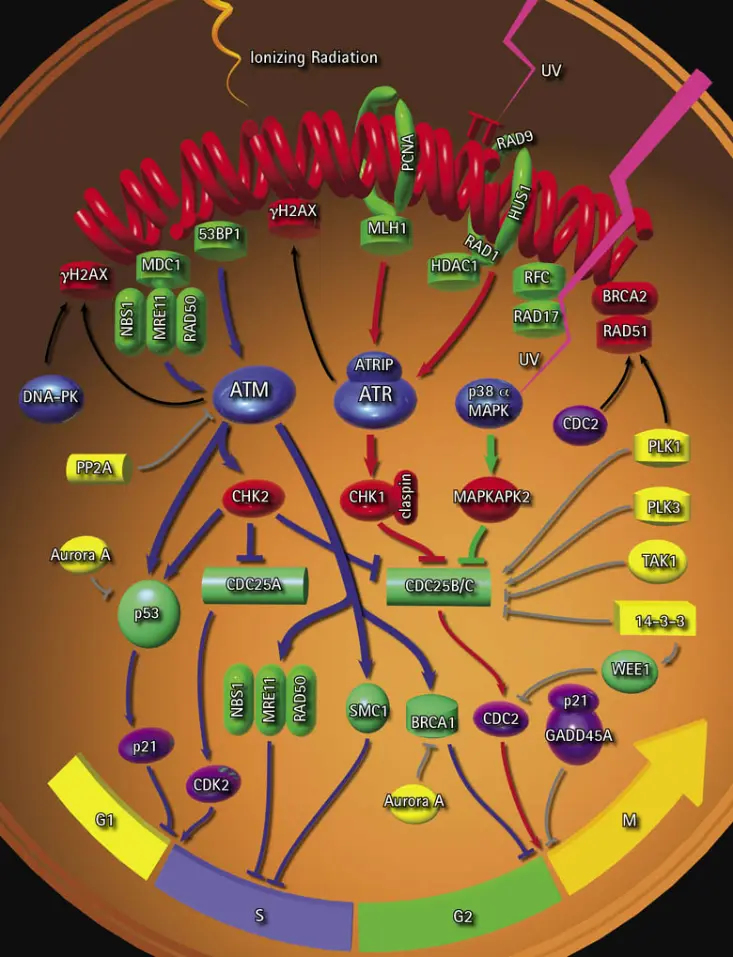
Checkpoint Signaling and DNA Repair
Checkpoint signaling and DNA repair are vital processes that ensure cells maintain their integrity. Checkpoint signaling regulates the cell cycle, allowing cells to monitor and respond to DNA damage or replication issues. Proteins such as p53 and ATM are involved in detecting DNA damage and activating repair mechanisms. If the damage is not too severe, these checkpoints can pause the cell cycle to allow time for repair.
DNA repair involves various pathways like homologous recombination and non-homologous end joining. These mechanisms fix DNA breaks or errors by either directly repairing the damaged DNA or using a template for accurate repair. The proper functioning of checkpoint signaling and DNA repair pathways is critical for cellular stability and preventing mutations.